We have seen in previous chapters that energy is one of the fundamental concepts of physics Heat is a type of energy transfer that is caused by a temperature difference, and it can change the temperature of an object As we learned earlier in this chapter, heat transfer is the movement of energy from one place or material to another as a result of a · • The work required is W = mgh, g and the change of potential energy per unit mass is gh • Thus level surfaces are surfaces of constant geopotential, where the geopotential is Work = mgh M M M M M Φ= ghG = (1/2)mv2 U g Set y = 0 at the bottom of the bowl Then 00mgr = (1/2)mv2 b 000 In this equation, the "00" is the K at the top, which is zero because the flake is released from rest The "000" is the U g at the bottom, which is zero because we chose y = 0 at the bottom Solve for v b v b = √ 2gr = p (2·98 m/s2)(022 m
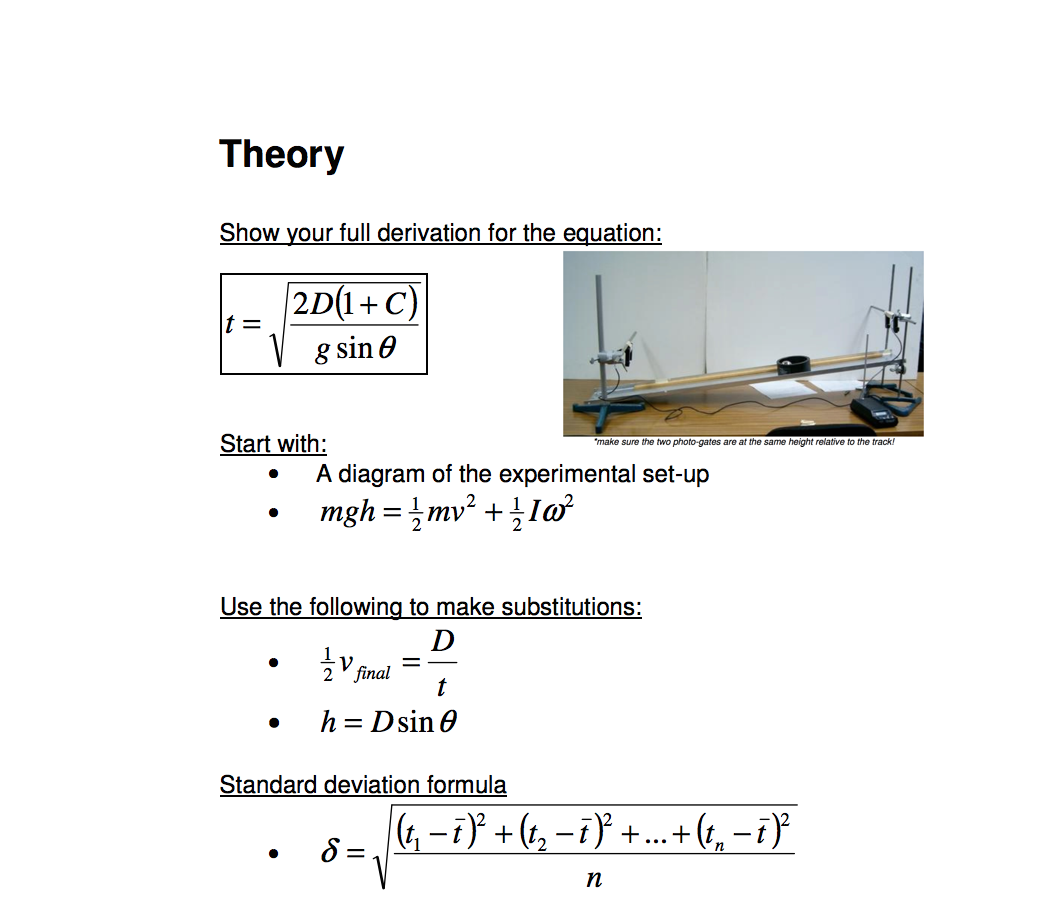
Solved Theory Show Your Full Derivation For The Equation Chegg Com
W=mgh solve for g
W=mgh solve for g-G g f f f q q cos 2 1 2 1 2 1 cos 0 0 0 2 0 2 0 2 = • = = = = D = = = = = = • = F v F s t where W = work F = force s = displacement F • s = scalar product of force and displacement KE = kinetic energy v = velocity or speed m = mass PE = potential energy (denoted as U on the AP Physics exam) g= acceleration due to gravity h = height above some reference point P = power = timeW = mgh Dragging that brick Assuming g=10 meter/sec 2, the weight mg of a 70 kg personthe pull of gravity on that personis about 700 newtons The energy of one calorie is therefore enough to raise him or her by about 6 meters (6 x 700 = 40 joule) Of course, if the efficiency of converting the chemical energy of food to muscle energy is only 10%, the person would only rise



Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 4 Work And Energy Free Pdf
Solve for a 050 2 (16 )( ) 981 551 ;The Pluto orbits the Sun in a fairly elliptical orbit once every 90;465 daysConcise Physics Part II Selina Solutions for Class 10 Physics ICSE, 2 Work, Energy and Power All the solutions of Work, Energy and Power Physics explained in detail by experts to help students prepare for their ICSE exams
Work is the energy transferred into or out of a system through the action of a force Work done against gravity can be found using the equation Work equals Force times height or W = Fh Since F = mg we can use the equation W = mghThe procedure to use the potential energy calculator is as follows Step 1 Enter the mass, acceleration due to gravity, and height in the input field Step 2 Now click the button "Calculate Potential Energy" to get the Energy Step 3 Finally, the potential energy of the body will be displayed in the output fieldFind out what is the full meaning of MGH on Abbreviationscom!
Gravitational potential energy is one type of potential energy and is equal to the product of the object's mass (m), the acceleration caused by gravity (g), and the object's height (h) as distance from the surface of the ground (the body) In this example, a 3 kilogram mass, at a height of 5 meters, while acted on by Earth's gravity would have 147G g f f f cos 2 1 2 1 2 1 cos 0 0 during free fall to solve for quantities such as speed or initial height U top K top = U bottom K bottom mgh top ½ mv top 2 = mgh bottom ½ mv bottom 2 The sum of the kinetic and potential energies of a system is called the total mechanical energy of the system These same principles can be applied to a block sliding down a frictionless ramp, a · You're given the equation W = mgh, where m is the mass in kg, g is the gravitational acceleration in m/s^2, h is the height in meters, and W is the



10 Check The Relation Mgh Mv T Using Dimensional Analysis Where Every Letter Has Its Usual


Acceleration Due To Gravity Questions And Answers Topperlearning
Pretty sure what you're referring to here is the gravitational potential energy U = m g h, where m is the mass of an object in kilograms, g is the acceleration due to gravity near the surface (usually taken to be 98 m/s on Earth), and h is the distance from the surface of the Earth (or some other reference point) It represents the potential energy the object gains from lifting the object to thatThe amount of work done is w = mgh, which is exactly equal to the amount of potential energy gained PE = mgh As the coaster begins to descend hill A, it loses potential energy (PE) and gains kinetic energy (KE), the energy of motion In a sense, the coaster is "trading in" PE for KE At point B, which is a little higher than the origin of the coaster, most of the PE has been converted to KEEnergy Energy changes forms without loss or gain The law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change forms Chemical energy is converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite



Nano Fe And Mg2ni Derived From Tma Tm Tm Fe Ni Mofs As Synergetic Catalysts For Hydrogen Storage In Mgh2 Sustainable Energy Fuels Rsc Publishing



How We Prove That Mgh 1 2mv2 Youtube
The equation Δ PE g = mgh Δ PE g = mgh size 12{Δ"PE" rSub { size 8{g} } = ital "mgh"} {} applies for any path that has a change in height of h h size 12{h} {}, not just when the mass is lifted straight upCalculate the work done, W=mgh for a mass of 300 g Then, using the accepted value for the specific heat of water, calculate the change in heat, Q=CMAT for the same data point a) Calculate the ratio WQ b) Suppose scale used to measure the mass of 300 g was not properly zeroed, and the mass was, in fact 350 g Recalculate the ratio W/Q c) Compare the ratios from part a) and b) DoSTRATEGIC INTERACTION MATERIAL (SIM) Physics STATE THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL WORK Solve for the work, energy and power done by an object TABLE OF CONTENTS TILE CARD 3 GUIDE CARD 4 ACTIVITY CARD1 6 ACTIVITY CARD2 8 ASSESSMENT CARD 9 ENRICHMENT CARD 10 REFERENCE CARD 11 ANSWER CARD 12 3 Work


Frontiers Magnesium Hydride Mediated Sustainable Hydrogen Supply Prolongs The Vase Life Of Cut Carnation Flowers Via Hydrogen Sulfide Plant Science



A Heat Flow In Dsc And B Mass Loss In Tg For Mgh 2 Processed By Hpt Download Scientific Diagram
In part a, W= mgh Note that if we use the exact form of the gravitational force, F(r) = Gmm=r2, then the work done on will be somewhat LARGER in c than in a Both of these answers are acceptable as long as they are explained!Remember the discussion above — lifting a mass against gravity requires power, and power applied over time requires energy The difference between power and energy is a Calculus idea (energy is the time integral of power), but it's not necessary to understand much Calculus to grasp this ideaW=mgh to lift the barbell so mgh=Ef The energy of a mass is increased by an amount mgh when it is raised by a height "h" Slide 31 / 112 Gravitational Potential Energy The name for this form of energy is Gravitational Potential Energy (GPE) GPE = mgh One important thing to note is that while changes in gravitational potential energy are important, their absolute value is not Slide 32



Ch 6 Work And Enery



Activity 11 15 An Object Of Mass Kg Is Dropped From A Height Of 4
Solve problems involving heat transfer;Solution for W=mgh equation Simplifying W = mgh Solving W = ghm Solving for variable 'W' Move all terms containing W to the left, all other terms to the right Simplifying W = ghmThe gravitational force, on the other hand, does perform work on the ball, according the height it reaches Since the radius of the circle is 2 m, the ball reaches a height of 4 m, and experiences work from the gravitational force of mgh = 2mg


Frontiers Magnesium Hydride Mediated Sustainable Hydrogen Supply Prolongs The Vase Life Of Cut Carnation Flowers Via Hydrogen Sulfide Plant Science



Activity 11 15 An Object Of Mass Kg Is Dropped From A Height Of 4
· 3) W=mgh m=W/(gh) 80kj = 80 000j 40mm = 004m m=80 000j/(98m/s^2 x 004m) = 4 kg 4) I'm not sure if 5mn is meaning 5 millinewtons or if it's a typo So I'm going to assume that it's not If it is a typo, let me know and I'll show how to solve it W=Fd d=W/F 5mn = 0005n 0kj = 0 000j d=0 000j/0005n = 40 000 000mEg pushing a door to open it or close it 2 Change the state of motion; · In physics, for the formula Work = Mass x Gravity x Height Is mass measured in kilograms, and height in metres?
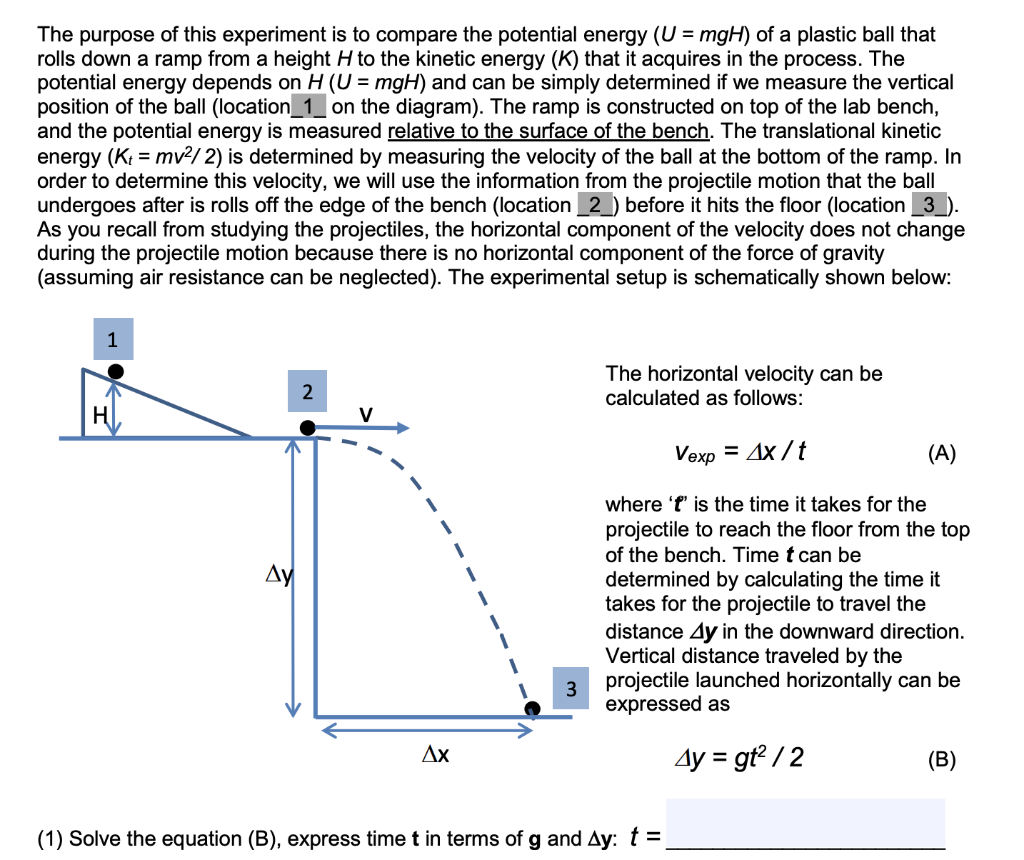


Solved The Purpose Of This Experiment Is To Compare The P Chegg Com



Statement I Work Done In Moving A Body Over A Smooth Inclined P
Ideal gas a gas whose particles exhibit no attractive interactions whatsoever; · Newton's second law states F = m*a, in which a is the acceleration In the case of gravitation, a = g = 9,1 m/s² Work = W = F*s In case of gravitation, F = m*g, and s could be represented by h (height) The work done equals the change of potential energy So potential energy U = W = mgh1 1 r r r r m s I kg m mr kg F mgmg T Img I mg I a a g a m m m m m mr g m a s (115) 15 A thinwalled hollow tube rolls without sliding along the floor The ratio of its translational kinetic energy



10 2 Work Ppt Download



Work Energy And Power Physics Summary Hs Tutorial
G = Fdcos θ = 350 N×0 m× workSenergy"theorem"net 0, or 700 J W =W s W f = W s = "(d)U se"the"equation"W Fdcosθ s = ,"where θ= 25°,and"solve"for"the"force" College"Physics" Student"Solutions"Manual" Chapter"7" " 55" " 3862 N 386 N 0 m cos25 700 J cos s = = × ° = = d θ W F " (e)"Since"there"is"no"change"in"speed,"the"work"energy"theorem"says"that* The relevant formula (w = work, m = mass, g = gravity, and h = height) is * w = mgh */ # include < stdioh > # define GRAVITATIONAL_CONSTANT = 98;5 Replace each Δ value with, eg, (KE 2 – KE 1) 6 Cross out each energy value that is equal to zero 7 Replace each energy term with its formula and solve Notes For "the work done by gravity," use W = mgh For "the work done by the spring," use W = ½ k x2 If the question asks for the work done by any other force, use W = F d cosθ



The Force Exerted By The Earth On A Particle Of Mass M A Distance R From The Centre Of The Earth Has The Magnitude Gme M R 2 Mgre 2 A Calculate The Work



Kinetic Energy Calculations Easy To Super Hard Ek 1 2mv 2 Youtube
3 Calculate the work done, W=mgh for a mass of 300 g Then, using the accepted value for the specific heat of water, calculate the change in heat, Q=cm WAT for the same data point a) Calculate the ratio W/Q b) Suppose scale used to measure the mass of 300 g was not properly zeroed, and the mass was, in fact 350 g Recalculate the ratio W/Q c) Compare the ratios from · (v) Work done by the force of gravity on a particle of mass m is given by W = mgh where, g is acceleration due to gravity and h is height through which the particle is displaced (vi) Work done in compressing or stretching a spring is given by W = \(\frac{1}{2}\)kx² where, k is spring constant and x is displacement from mean positionJust wanting to check before I hand in my homework )



Ap Physics 1 Finding Velocity In Terms Of Variables Through Co Derivation Of Energy Homeworkhelp



Solved Theory Show Your Full Derivation For The Equation Chegg Com
= g newton 1 kgf = 98 newton Solution 17 It means that 1 kgf or one kilogramme force is the force due to gravity on 1 kilogram mass Solution 18 Effects a force can produce and examples 1 Change the state of rest;Calculate the energy needed for moving a mass of 4kg from the centre of the earth to its surface If radius of the circle is 6400km and acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth is g= 10m/sSolve each equation for the variable specified 5 11 14 y mx b, for b 5xy n = —6, for y 3x 4y = 7, for y W = mgh, for g 3 f — epd, for e 10 13 for t 12g 31h —8", for h 3x y = 4, for c bc — 2y, for y 6y z = 6 9 12 15 17 v = r at, for r m n = 3, for m t), for n for r 16 18 42s), PV nRT, for V 6t 62s = —(3t D, for D 3c5d= 7d — 6c, for d Answers
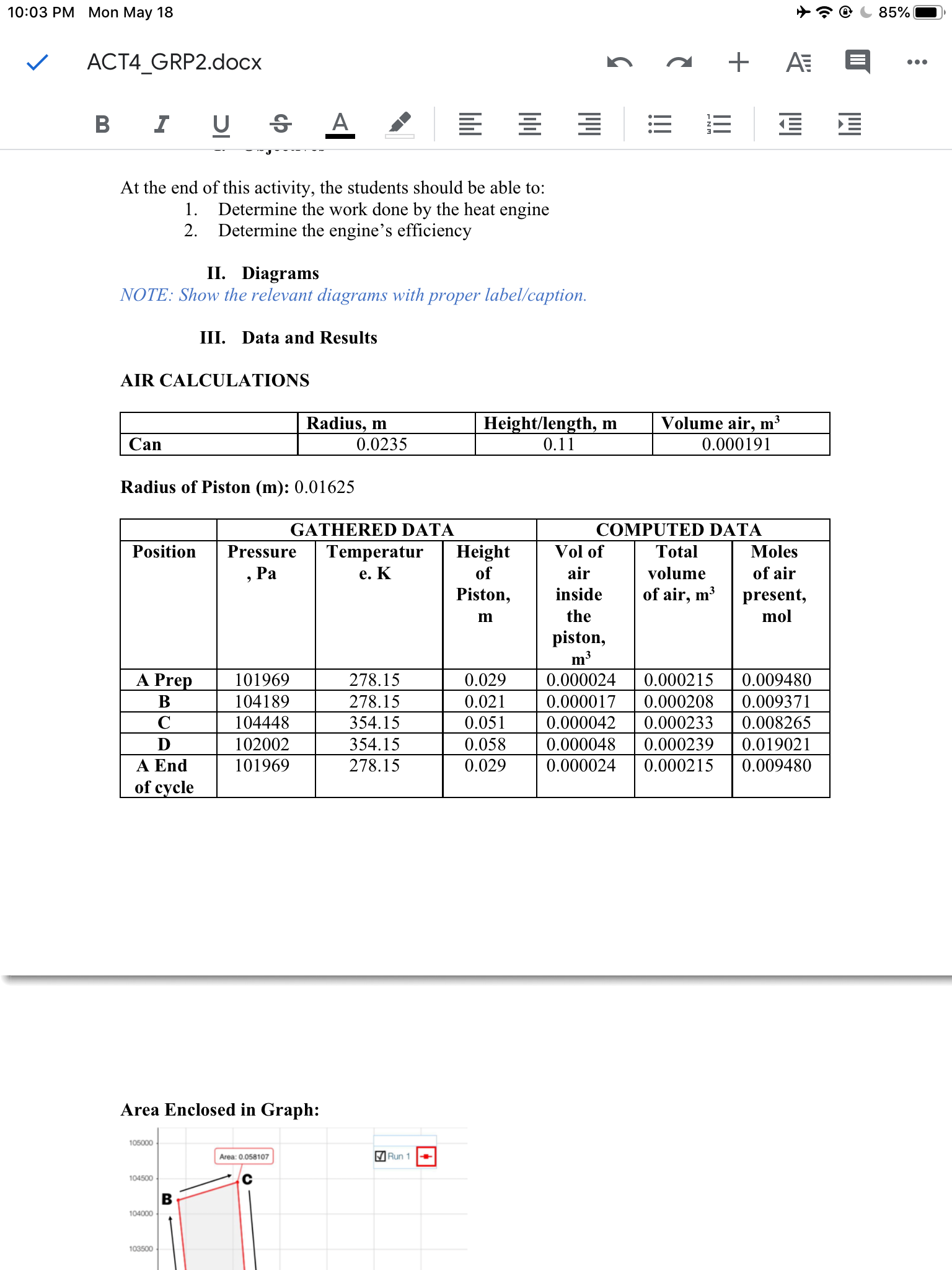


Answered Calculate The Actual Work Done On The Bartleby



Consider An Equation 1 2mv 2 Mgh Where M Is The Mass Of The Body V Its Velocity G Is The Brainly In
· The work done by gravity is given by the formula, Wg = mg (∆ h) Where, m = mass, g = gravity, h= height The negative sign shows that the particle is dropping from a height Δ h vertically in the direction of gravityFor example when a 10 kg book is lifted 05 m from the table, the force exerted in lifting the book is equal to its weight F=weight=mg The acceleration due to gravity, g is equal to 98 meters per second squared The work done in lifting the book is W=Fd where the displacement (d) is the height (h) to which the object is lifted W=mgh 51W= Force × displacement =Weight × height = mg × h Thus, work done by force of gravity, W =mgh Similarly, if the body is thrown up to a height h, the work done by gravity is W = mgh
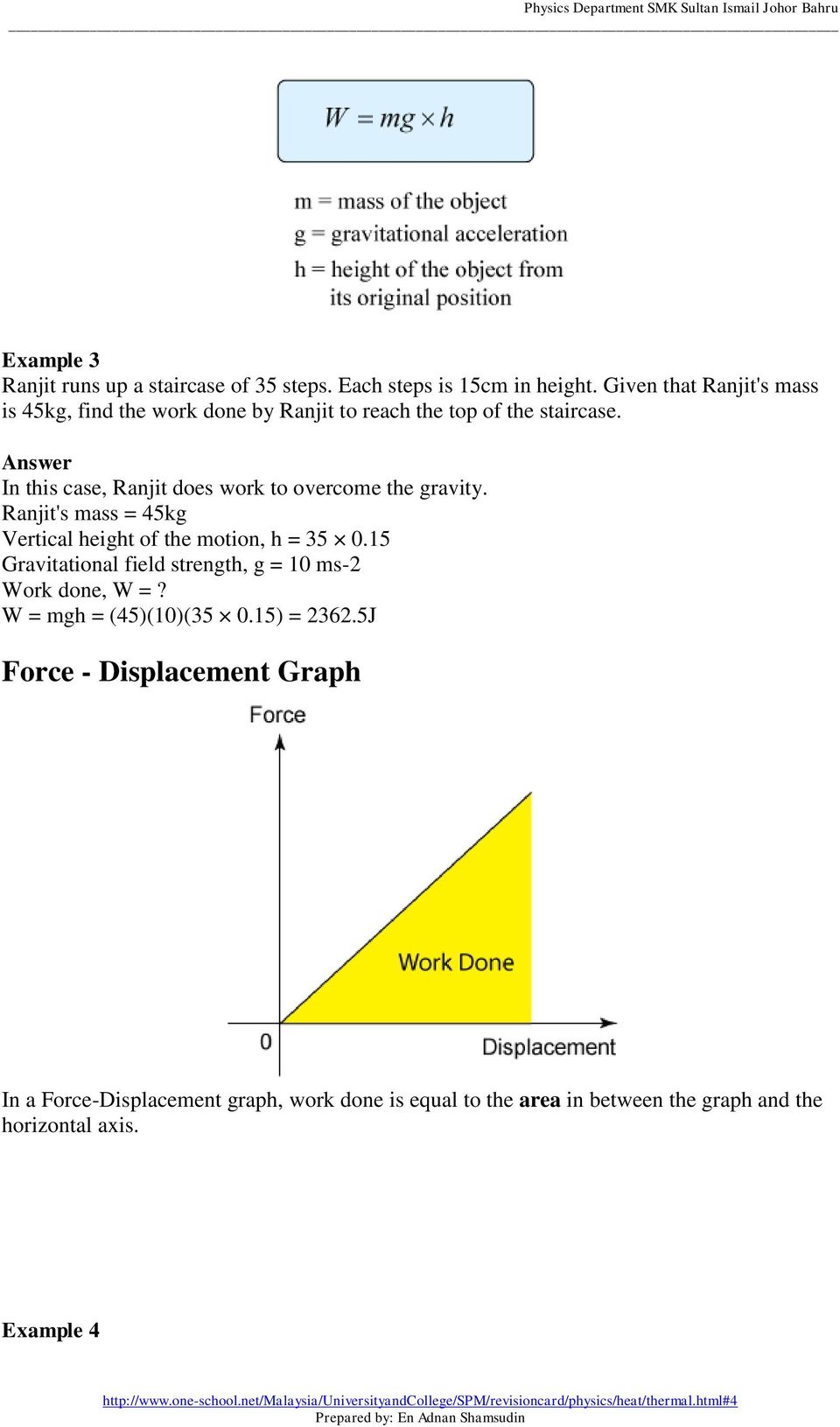


Weight The Weight Of An Object Is Defined As The Gravitational Force Acting On The Object Unit Newton N Pdf Free Download



Science Essay December 14th Ppt Download
· I have a Physics question about the work done on a raindrop as it falls vertically for a distance of (45)m The rain drop falls at a constant velocity of (18)ms^1, and has a mas of (72x10^9)kg I have to work out the Work Done I have the formula for Work Done as, W = F s cos (theta) and using this I got the answer (365x10^7) But apparently the actual answer wasThe change in gravitational potential energy, ΔPE g, is ΔPE g = mgh, with h being the increase in height and g the acceleration due to gravity The gravitational potential energy of an object near Earth's surface is due to its position in the massEarth systemUse g = 10 m/s2 in this problem (a) You drop a 40 kg block from rest, and it falls through a height of 50 cm Calculate the work done by the force of gravity on the block



Ppt Work Power Energy Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
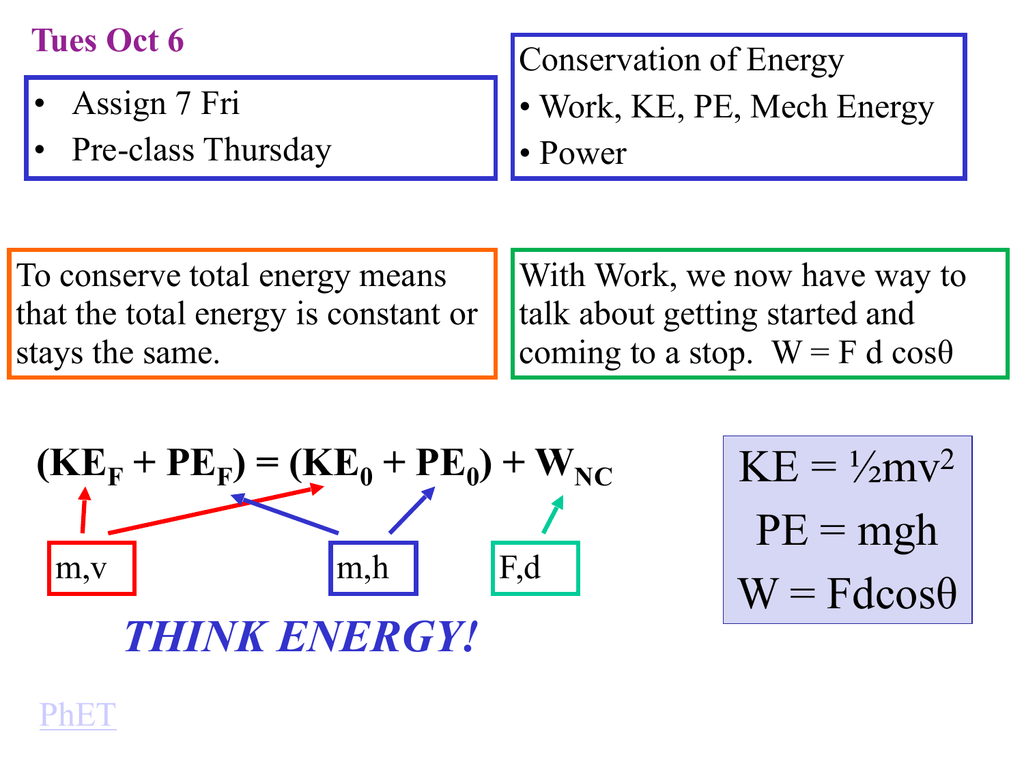


Think Energy Ke Mv2 Pe Mgh W Fdcos8
Apply the ideal gas law to solve problems in chemistry Key Takeaways Key Points An ideal gas exhibits no attractive forces between particles In the ideal gas equation, both pressure and volume are directly proportional to temperature Key Terms ideal gas constant R = 145 J·mol1·K1;Physics Calculators, Also tutorials, formulas and answers on many physics topics · Because the mass, height and g(99m/s^2) are the same in both cases, the answer will be 1m/s Well, in both cases, the work done has the same magnitude (but opposite sign) However, the work done is the change in kinetic energy, which



Ith Watet Quid Is Way With Uniform Ac Mixed With Womghy Without Di Miled In W



Conservation Of Energy Video Khan Academy
'Massachusetts General Hospital' is one option get in to view more @ The Web's largest and most authoritative acronyms and abbreviations resourceEg applying a force to stop the cricket ball 3 · w=mg stands for weight = (mass) x (acceleration of gravity) here on earth acceleration of gravity equals 98 m/s/s so if you want to calculate the weight of something here on earth and if the mass was 10g the weight would me 98 because w=mg w= (10) (98) answer 98 newtons Show more



Solved I Need Help Fixing And Solving These 3 Problems In Chegg Com
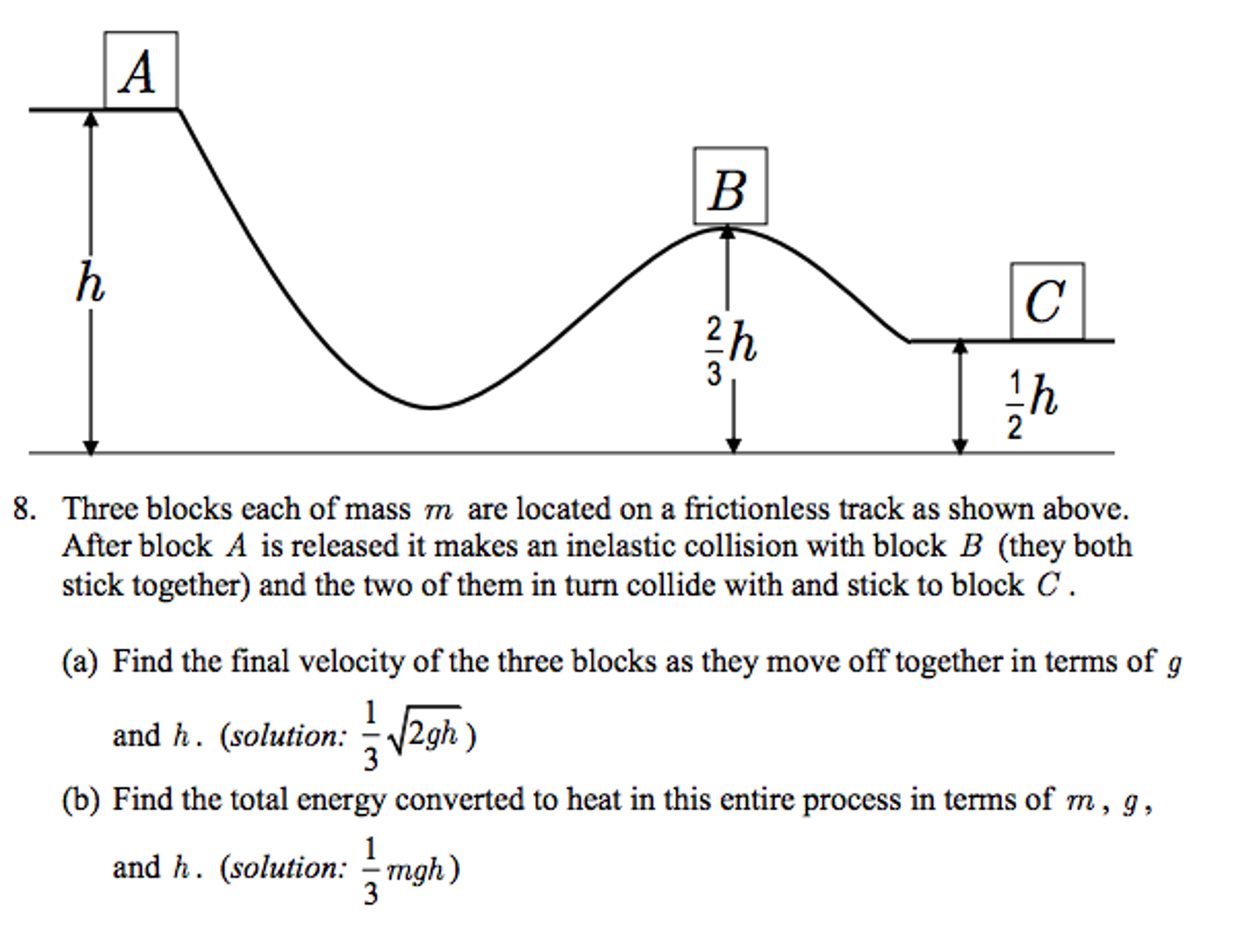


Solved Please Answer Part A And B And Show All Algebra W Chegg Com
· Objective To have only one h and for it to be on its own on one side of = and everything else on the other side Change m and g into 1 so that h is on its own Divide both sides by mg giving P mg = mgh mg P mg = m m × g g × h But m m and g g both = 1 P mg = 1 × 1 ×h h = P mg Answer linkPhysics Formulas Get list of all Physics formulas here at CoolGyanOrg prepared by subject expert teachers Also Download the Chapter wise Important Maths Formulas and Equations to Solve the Problems Easily and Score More Marks in Your CBSE Board ExamsLooking for the definition of MGH?



Solved Uinitial Kfinal Or Mgh Motorov Eq 11 Pre Lab Chegg Com



In Situ Catalyzed And Nanoconfined Magnesium Hydride Nanocrystals In A Ni Mof Scaffold For Hydrogen Storage Sustainable Energy Fuels Rsc Publishing
A Solve the formula d rt for t The variable t has been multiplied by r, so divide each side by r to isolate t or t Thus t , where r 0 b Find the time it takes to drive 75 miles at an average rate of 35 miles per hour Use the formula you found for t in Example A t d r t Use dimensional analysis t 2 hours1 7 75 mi 35 m h i d r d r rt r t# define MASS = 1000;Int main (){ double MASS, GRAVITATIONAL_CONSTANT, HEIGHT, WATER;



Pls Solve An Iron Nail Is Dropped From A Height H From The Level Of A Sand Bed If Physics Laws Of Motion Meritnation Com



3 Find Speed Ofend A When It Is At Point B A 25 1 H In 9 0 2gh In A 6 Van 1 2 A P3sh 1 4 14 Find Max Kinetic Energy Of Chain Before End
W mgh d W mgh sin SOLVE The mathematical representation is based on the law of conservation of mechanical energy ASSESS Check that your result has the correct units, is reasonable, and answers the question 53 Speed in a vertical circle with friction Consider how things change when friction is introduced 54 Speed in a vertical circle with friction How much



Notes On Work Enegry Power Notes



Learn Ap Physics Ap Physics 1 2 Work And Energy
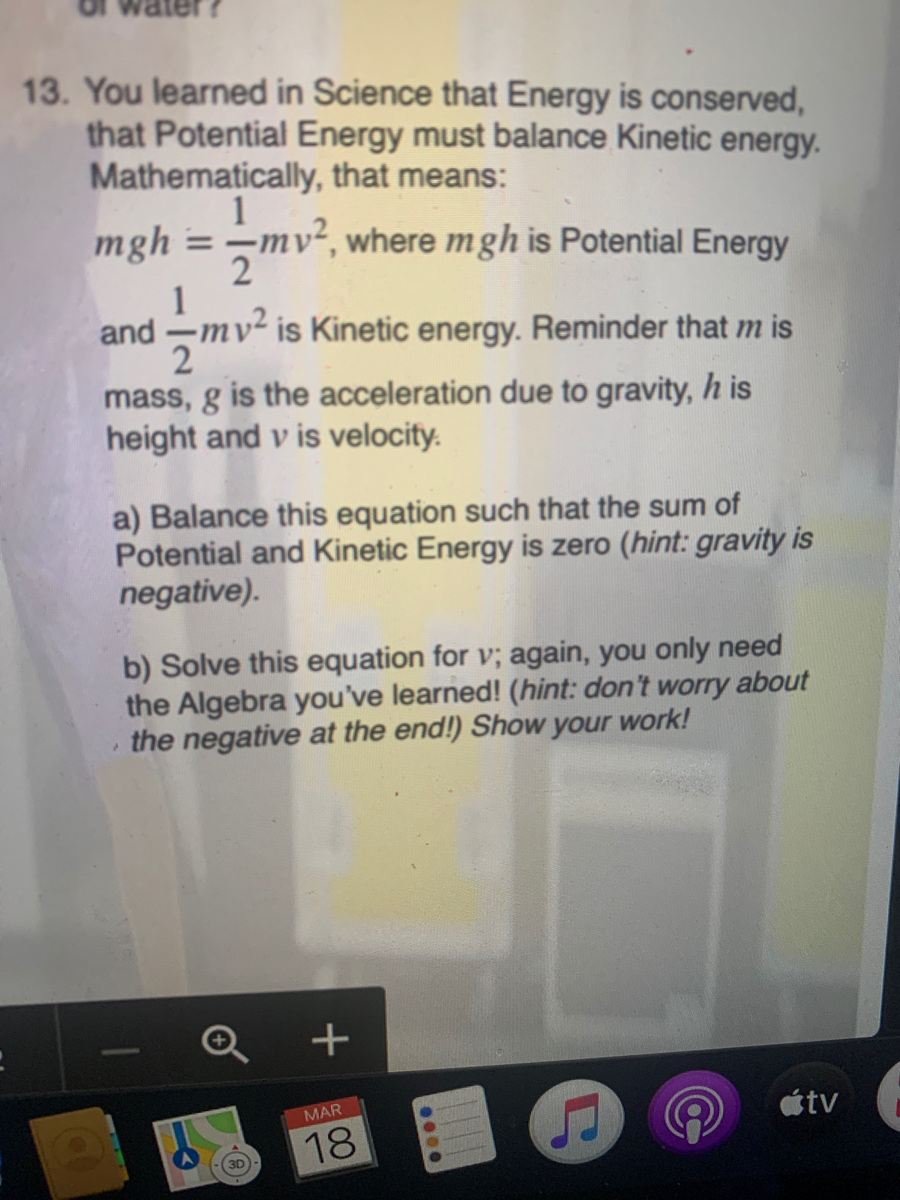


G In Mgh



2 A Body Of Mass M Is Raised To A Height H From The Surface Of The Earth Where The Acceleration Due To Gravity Is G Prove That The Loss In Weight



Ethiopia Learning Physics Grade 7 Page 96 In English



Vertical Springs And Energy Conservation Video Khan Academy



Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 4 Work And Energy Free Pdf



Energy Examples Dean Baird S Phyz Home Page
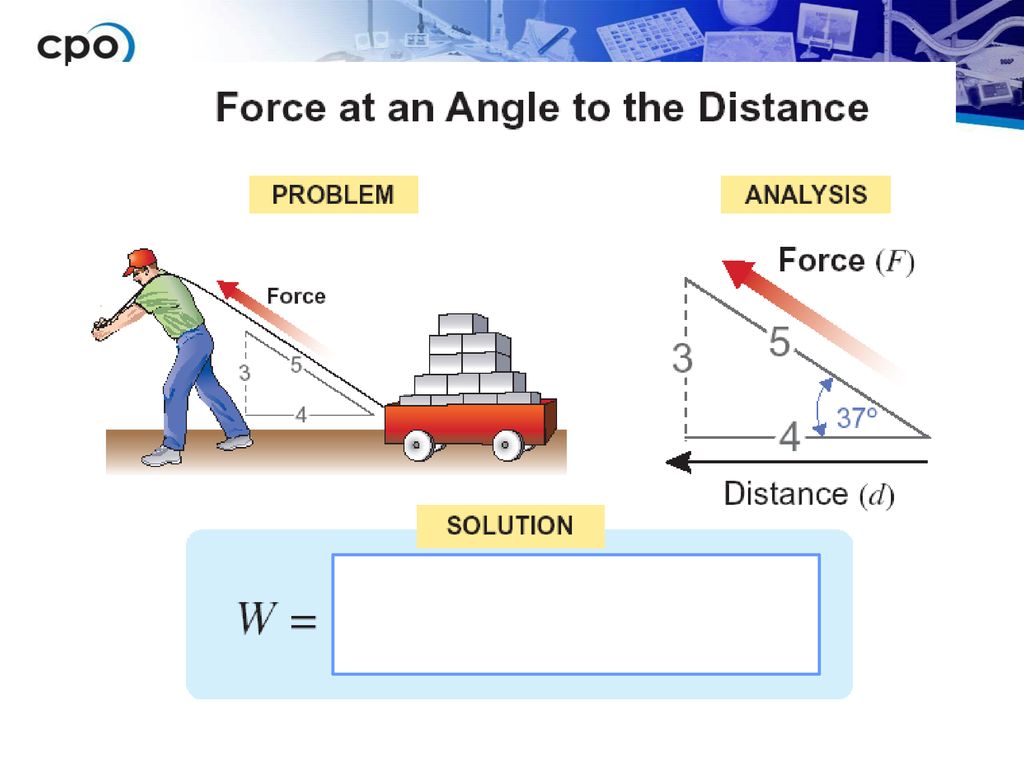


Foundations Of Physics Ppt Download



Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 4 Work And Energy Free Pdf



10 2 Work Ppt Download



Chai Gr C 92 Pdf Txt



Foundations Of Physics Ppt Download
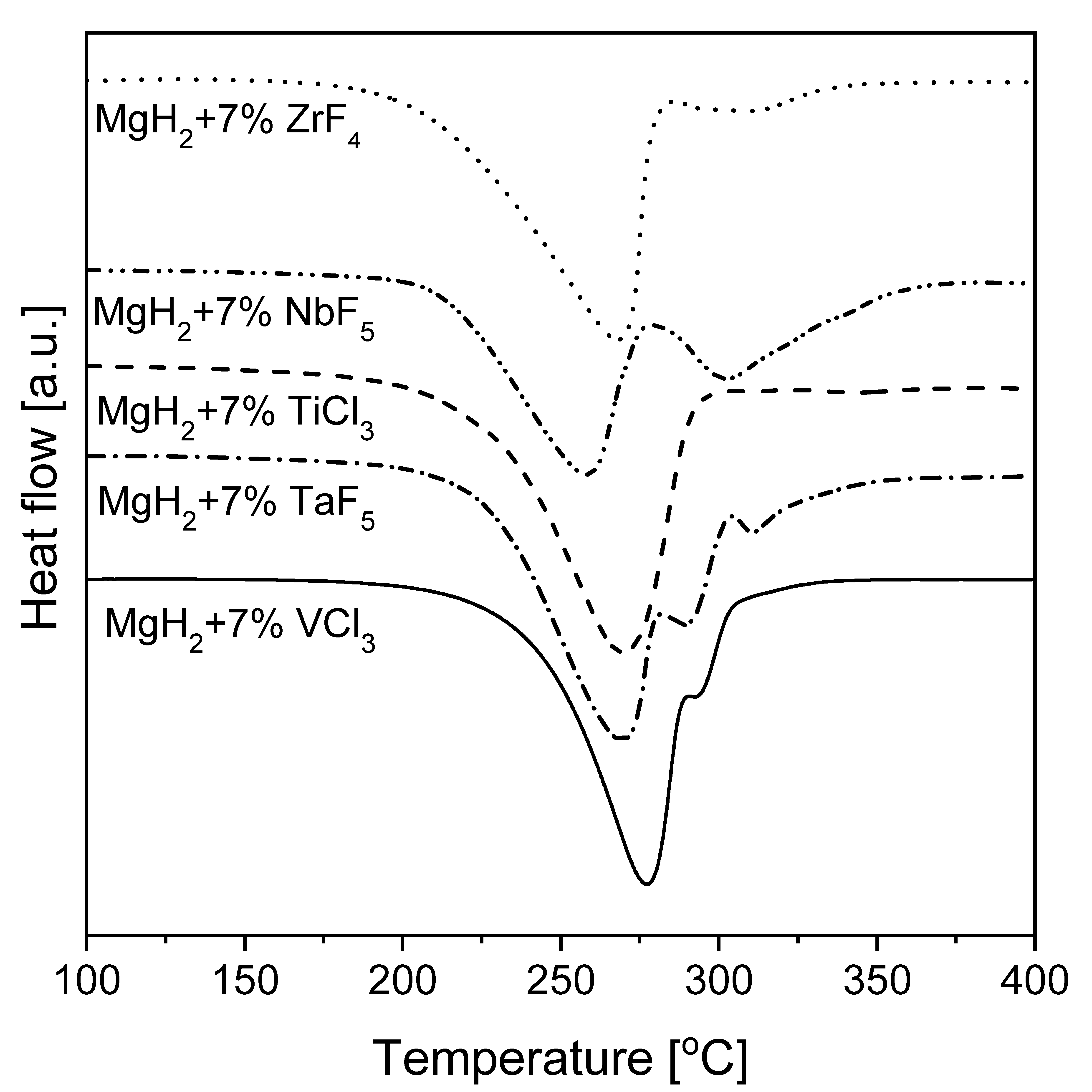


Vxsc4t5txetxcm



Solved Angle Between The Force And The Displacement Is Gi Chegg Com


Analytical Mechanics For Students Of Physics And Engineering Ation We Havei Co Mga Sin A Energy Method In Movingthrough A V Distance S Aloii Ti Theplane The Potential Energy Of


How High Would You Have To Th See How To Solve It At Qanda



A Helicopter Lifts A 72 Kg Astronaut 15 M Vertically From The Ocean By Means Of A Cable The Acceleration Of The Astronaut Is Frac G 10 How Much Work Is Done On



Check The Correctness Of Equation 1 2 Mv2 Mgh Brainly In



How To Solve Solution Please Brainly In



Let Us Consider An Equaiton 1 2 Mv 2 Mgh Where M Is The Mass Of The Body Upsilon Its Youtube



D W A Player Hits A Football The Ball Moves Along A Curved Parar Work Done By The Force Of Gravity On The Ball Is Mass Of Ball Is M And



Prove Potential Energy P E Mgh With Figure Brainly In



A Body Of Mass M Is Raised To Aheight H From The Surface Of The Ea



Ght H Leration Due To Gravity 8 9 8 Ms 2 M E Work Is Physics



Htpib06c Calculating Gravitational Potential Energy Using Ep Mgh Youtube



Htpibreview Ch6 P Mgh T Example Youtube



An Athlete Mass 60 Kg Skips At The Rete Of Steps Per Minute



Answered The Equation Used To Solve For Bartleby



Chapter 11



Work And Conservation Of Energy Pdf Free Download



Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 4 Work And Energy Free Pdf



Nano Fe And Mg2ni Derived From Tma Tm Tm Fe Ni Mofs As Synergetic Catalysts For Hydrogen Storage In Mgh2 Sustainable Energy Fuels Rsc Publishing



Power Problems And Solutions



Grade 11 Physics Nov 6 Gravitational Potential Energy



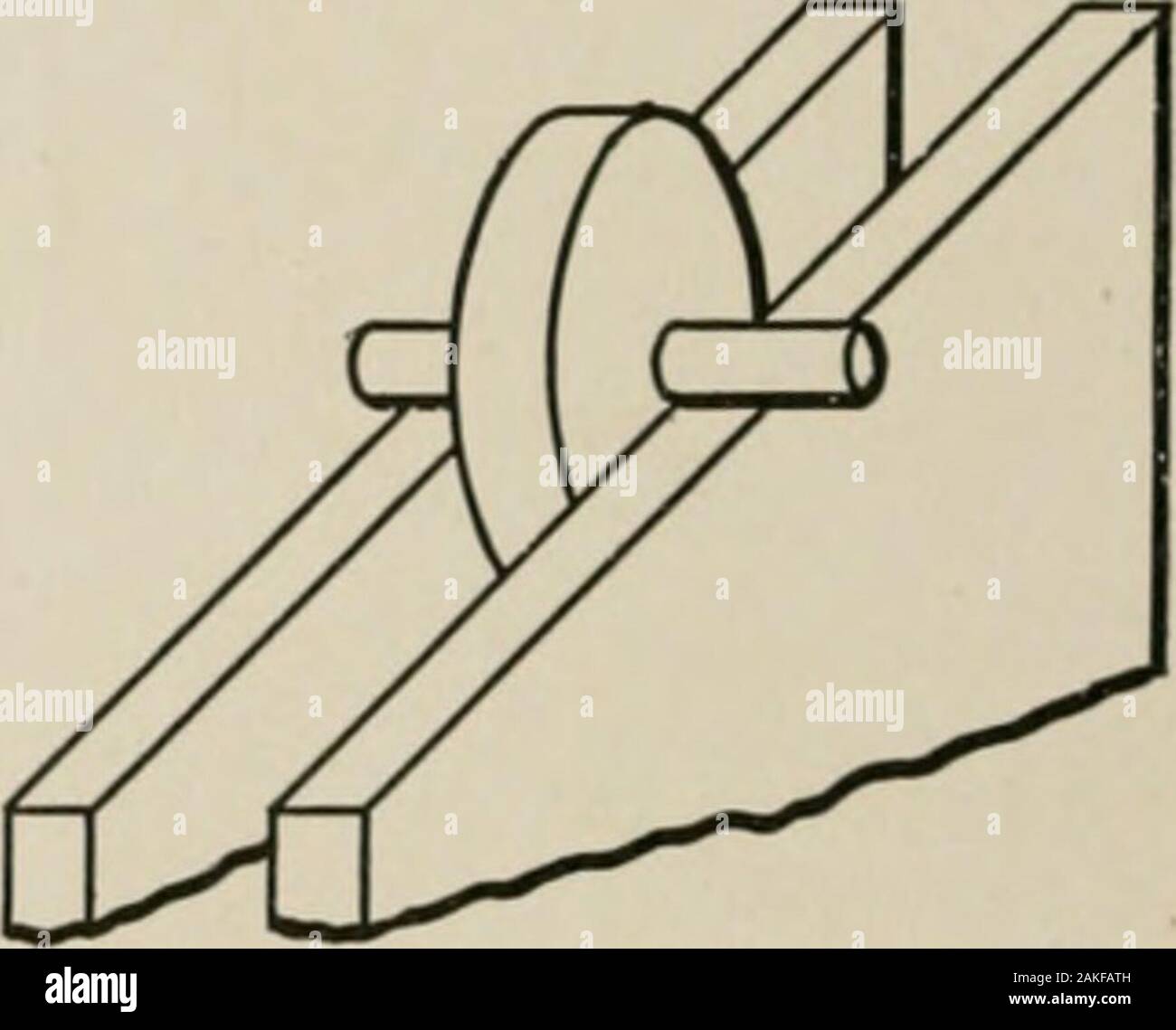
11 A Cord Is Wound Around The Circumference Of Wheel Of Radius R The Axis Of The Wheel Is Horizont And Moment Of Inertia About It Is T The Weight Mg Is



Ppt Physics 121 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Notes On Work Enegry Power Notes



A Body Dropped From A Height H Reaches The Ground With A Speed Of



Solved Average Speed Tota Distance Elapsed Time A Av Di Chegg Com



27 We 0 00 0 40 4 A Body Of Mass M Tied To A String Is Lowered At A Constant Acceleration Of G 4 Through A Vertical Distance H The Work Done By



Chapter 7 Work And Kinetic Energy Ppt Download



Gravitational Potential Energy Cie A Level Physics Revision Notes



Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 9 Solutions For Chapter 4 Work And Energy Free Pdf



Notes On Work Enegry Power Notes



Notes On Work Enegry Power Notes



Solved Av Total Distance Average Speed Elapsed Time Ax Chegg Com



General Physics 101 Phys Dr Zyad Ahmed Tawfik Ppt Download



Work And Energy Chapter 8 Mv 2 2 F 2 F3 Dr 4 P Dr F2 Dr F3 Dr 8 1 Kinetic Energy Pdf Free Download



Giancoli 6th Edition Problem Solutions Chapter 6
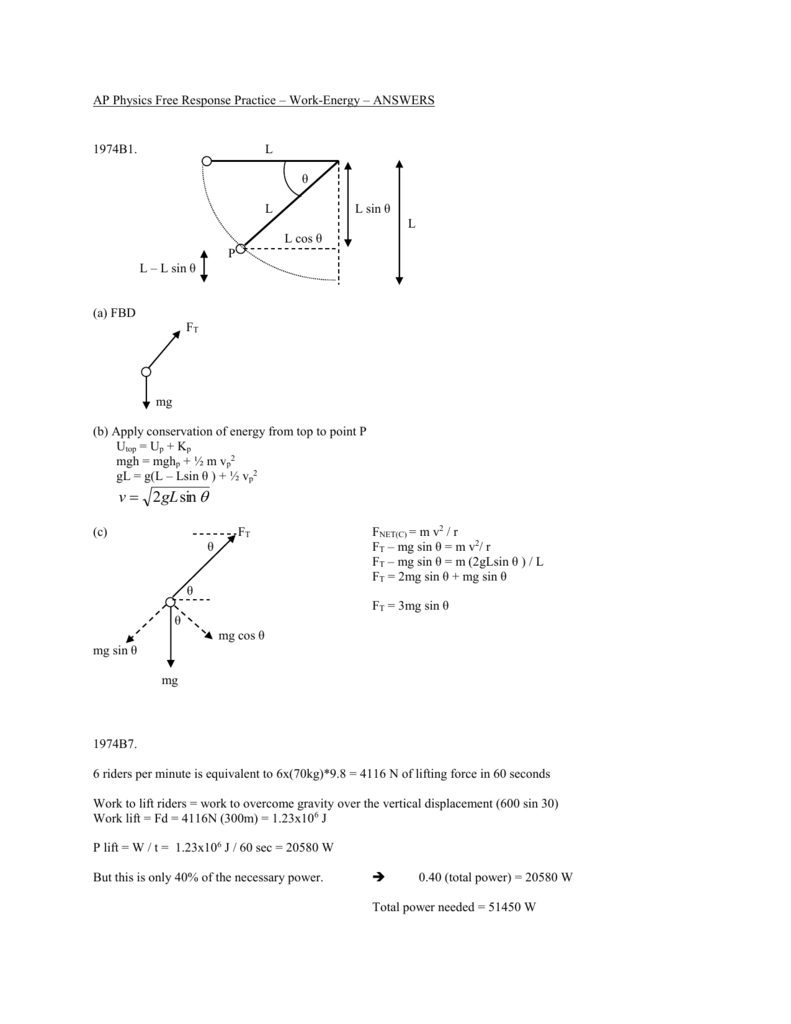


4d Work Energy Fr Practice Problems



Ls Thang Physics Home Facebook



Answered 1 Uinitial Kfinal Mgh Mv Iw 2 Or Bartleby



Law Of Conservation Of Energy Ppt Download



Prepared By A Science Intervention Material Science Iv Teacher Category Ppt Download



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿