The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring programAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsThe relative risk of a child developing ALL is child versus a stay at home child times as likely for a day caresocialized 233b) Calculate the sample odds ratio for the odds of a child developing ALL for a day care socialized child versus a stay at home child = 233c) Calculate a 95% confidence interval for the true odds ratio

Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08
Odds versus relative risk
Odds versus relative risk-For instance, a relative risk of 70% corresponds to an odds ratio of 07/(107)=233 however, it is clearer to say to the layman that a certain risk factor "increases the probability of a disease by 70%" (relative risk) rather than that it "increases the2) Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the nonobese Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download
Odds Ratio, Hazard Ratio and Relative Risk Janez Stare1 Delphine MaucortBoulch2 Abstract Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature Most readers perceive it as relative risk (RR), although most of them do not know why that would be true But since such perception is mostlyThe interpretation of an odds is more complicated than for a risk The simplest way to ensure that the interpretation is correct is to first convert the odds into a riskOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)
The homemade video abstract on the BMJ website shows you the difference between odds and risk, and how one odds ratio can mean several different relative risks (RRs), depending on the risk in one of the groups Unfortunately, in some situations, you just have to get an OR, notably logistic regression and retrospective casecontrol studies A 1 to 4 odds means there are five possible outcomes If you are interested in the blue card, it happens once among those five outcomes, or % of the time Likewise, relative risk makes a lot of sense The relative risk of picking a blue card in group A compared to group B is 1/3 or 033 We can understand that by looking at the pictureThe baseline risk is the denominator of relative risk, ie, the risk of the group being compared to In our example, this would be the risk of heart attack for the normal range If this baseline risk is high, then a relative risk of 5 would be alarming;
Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, notThe relative risk (RR) and the odds ratio (OR) are the two most widely used measures of association in epidemiology The direct computation of relative risks isIn the "risk" of response and a 60% increase in the "risk" of remission Risk, therefore, is used to reflect probability, regardless of the desirability or undesirability of an event 2 Relative risk is an important and commonly used Odds Ratio



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science
Odds ratio versus relative risk Since it is a ratio of ratios, the odds ratio is very difficult to interpret The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative risk is not very good and the odds ratio can be used Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinctionFor example, an odds of 001 is often written as 1100, odds of 033 as 13, and odds of 3 as 31 Odds can be converted to risks, and risks to odds, using the formulae;




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey




Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases
The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population, It is assumed that, if the prevalence of the disease is low, then the odds ratio approaches the relative risk Case control studies are relatively inexpensive and less timeconsuming than cohort studies In this case the odds ratio (OR) is equal to 16 and the relative risk (RR) is equal to 865Selfstudy oddsratio epidemiology relativerisk riskdifference




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table
Introduction and background Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios An example of what I am talking about is the choice between risk ratio and odds ratio Odds ratio vs risk ratio You know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjects Thus, we can calculate the risk of having a heart attack among smokers (infarcted smokers Risk vs odds The terms 'risk' and 'odds' are often used interchangeably but they actually have quite different implications and are calculated in different ways Odds is a concept that is very familiar to gamblers It is a ratio of probability that a particular event will occur and can be any number between zero and infinity




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
If the baseline risk is small, then a relative risk of 5 may not be too serious Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075 If the risks were 08 and 09, the odds ratio and relative risk will be 2 very different numbers OR = 044 and RR = 0 Relative risk vs Odds ratio




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
The simple relative risk is 055 and the simple odds ratio is 025Clearly the probability of fathering a child is strongly dependent on a variety of demographic variables, especially age (the issue of marital status was dealt with by a separate analysis) The control group was 84 years older on average (435 years versus 351), showing the need to adjust for this variable The relative risk is confused by some with the odds ratio and absolute risk Relative risk is the ratio of the probability of an event occurring with an exposure versus the probability of the event occurring without the exposure Thus to calculate the relative risk, we must know the exposure status of all individuals (either exposed or notThe relative merits of risk ratios and odds ratios Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 09 May;163(5) doi /archpediatrics0931 Author Peter Cummings 1 Affiliation 1 Department of Epidemiology, School of




Beabletocalculate Direct Age Adjustment Chegg Com




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
Odds ratio is similar to relative risk In the sheepskin trial the relative risk was 058 and the odds ratio was 054 For most clinical trials where the event rate is low, that is less than 10% of all participants have an event, the odds ratio and relative risk can be considered interchangeable The relative risk tells us the ratio of the probability of an event occurring in a treatment group to the probability of an event occurring in a control group It is calculated as Relative risk = A/ (AB) / C/ (CD) In short, here's the difference An odds ratio is a ratio of two odds Relative risk is a ratio of two probabilitiesRelative Risk (RR) & Odds Ratio (OR) The difference between odds and probability is important because Relative Risk is calculated with probability and Odds Ratio is calculated with odds Relative Risk (RR) is a ratio of probabilities or put another way it is one probability divided by another Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds



Forest Plots Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Detecting Fecal Download Scientific Diagram



Odds Vs Relative Risk ただの悪魔の画像
9222 Measures of relative effect the risk ratio and odds ratio Measures of relative effect express the outcome in one group relative to that in the other The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a)For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effectsOr, is there any condition to use the measures?The Relative Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio are both used to measure the medical effect of a treatment or variable to which people are exposed The effect could be beneficial (from a therapy) or harmful (from a hazard) Risk is the number of those having the outcome of interest (death, infection, illness, etc) divided by the total number exposed to




Relative And Absolute Risk Osmosis




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation Odds ratios work the same An odds ratio of 108 will give you an 8% increase in the odds at any value of X Likewise, the difference in the probability (or the odds) depends on the value of X So if you do decide to report the increase in probability at different values of X, you'll have to do it at low, medium, and high values of X Even with initial risks as high as 50% and very large reductions in this risk (odds ratios of about 01), the odds ratio is only 50% smaller than the relative risk (01 for the odds ratio compared with a true value for the relative risk of 02)




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube
A risk ratio is a good measure to use for a metaanalysis if you have data from longitudinal cohorts or clinical trials It is generally thought to be easier to interpret than an odds ratio Relative risk, odds ratio, risk ratio, risk difference these are all measures of the direction and the strength of the association between two categorical variables Can I use any of these four measures?Odds ratios have often been confused with relative risk in medical literature For nonstatisticians, the odds ratio is a difficult concept to comprehend, and it gives a more impressive figure for the effect However, most authors consider that the relative risk is readily understood




Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be
The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the Examples of measures of association include risk ratio (relative risk), rate ratio, odds ratio, and proportionate mortality ratio Risk ratio Definition of risk ratio A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group Table 1 Relative risk (RR) vs Odds Ratio (OR) vs Hazard Ratio (HR) HRs are in tandem with survivorship curves, which show the temporal progression of some event within a group, whether that event is death, or contracting a disease In a survivorship curve, the vertical axis corresponds to the event of interest and the horizontal axis



Github Flor3652 Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Shiny App



1
The null value is 1, and because this confidence interval does not include 1, the result indicates a statistically significant difference in the odds of breast cancer women with versus low DDT exposure Note that an odds ratio is a good estimate of the risk ratio when the outcome occurs relatively infrequently ( The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers RR = (a/ (ab))/ (c/ (cd)) = (a (cd))/ (c (ab)) Given that you know a, b, c, and d, you can compute either of these metrics Yet odds ratio is strongly preferred as the "right" metric to Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 table



Relative Risk Odds Ratio




Statistc 111 Lecture Notes Spring 19 Lecture 11 Odds Ratio Relative Risk Ert2
RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO The relative risk (also known as risk ratio RR) is the ratio of risk of an event in one group (eg, exposed group) versus the risk of the event in the other group (eg, nonexposed group) The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds of the event in the other group




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine



Epidemiology Stepwards




Solved Select All Of The True Statements Regarding The Odds Chegg Com




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像



Interpretation Of Odds Ratio And Fisher S Exact Test By Sergen Cansiz Towards Data Science




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



Relative Risk Odds Ratio




Kevin Whelan If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper



Odds




Glossary Of Research Terminology




Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Ratio And Why It Matters Youtube




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Measuring Of Risk



The Difference Between Probability And Odds




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Risk Estimates Relative Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio Analyses For Download Table




Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk



Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy On Vimeo




Literature Search




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Relative Risk Wikipedia




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio On The Backpack And Back Pain Study Massage Fitness Magazine




Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Extensive Video Youtube




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
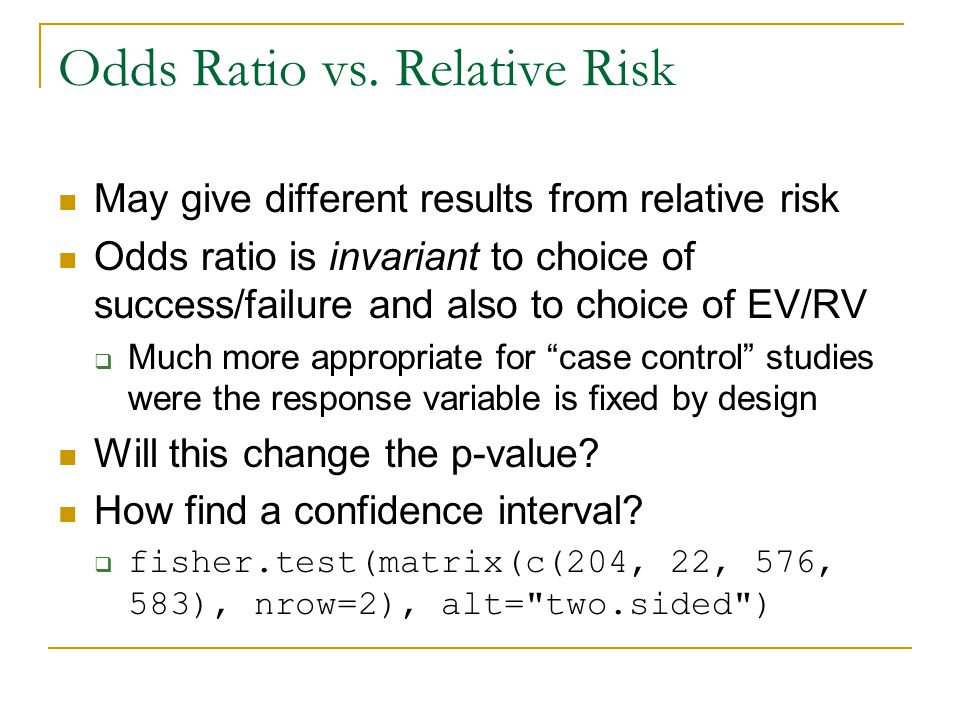



Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Calculation And Interpretation Of Odds Ratio Or And Risk Ratio Rr Youtube
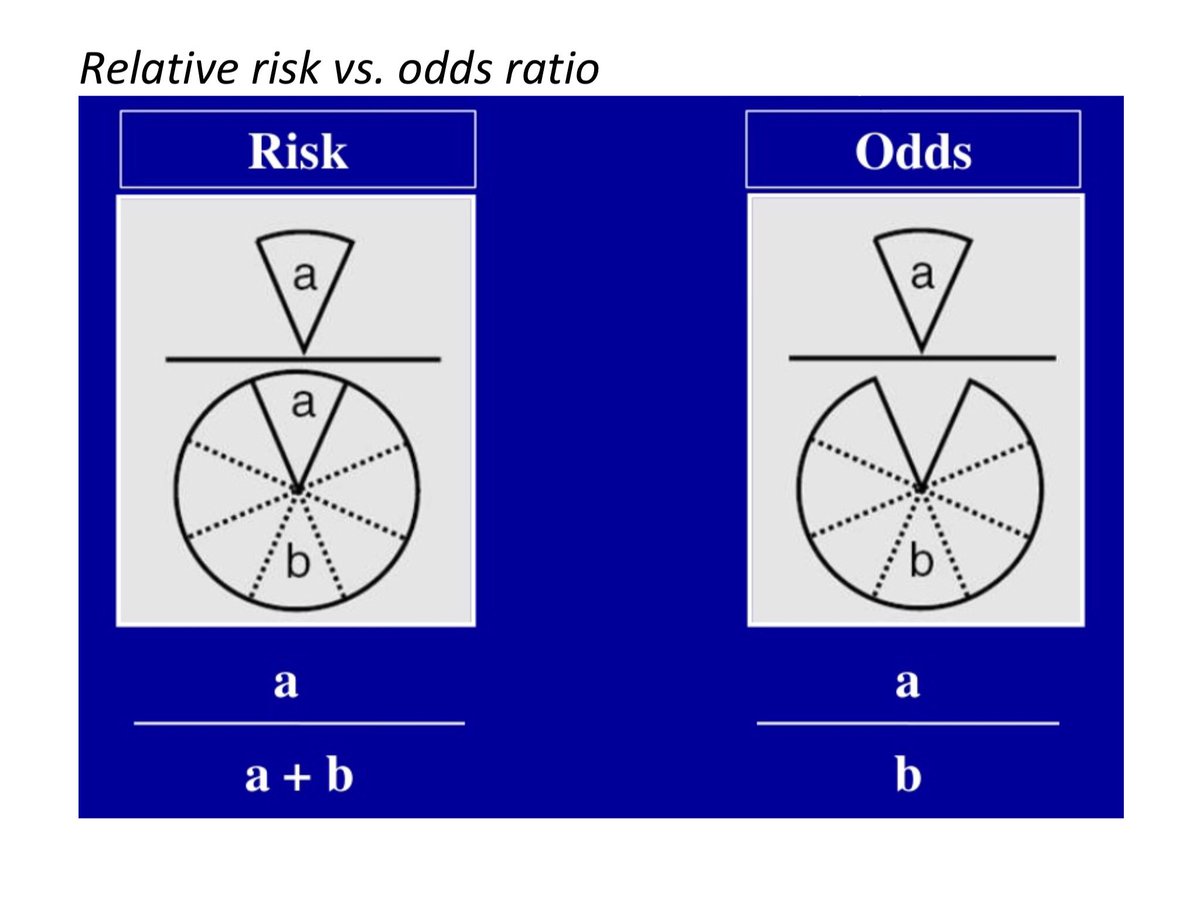



最新 Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Usmle ただの悪魔の画像




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar



6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Incidence And Prevalence Are Formally Defined On Slide 7 Birth And Death Rates Are Also Estimates Of Absolute Risk Risk Factors Are Identified By Determining




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Intervals For Download Scientific Diagram




Solved Activity 4 Identification Of Risk Relative Risk Chegg Com




Odds Ratio Article




Figure 2 X 2 Table With Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf



Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream




Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk What S The Difference Statology




Relative Risk Wikipedia



1




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk What S The Difference Statology




Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Youtube




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough




いろいろ Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk ただの悪魔の画像




Measures Of Association Stats Medbullets Step 1




Solved Present Example Of An Dolds Ratio Compared To A Chegg Com



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gpraj




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download




Statistics For Afp Dr Mohammad A Fallaha Afp




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Model Example Cpb Presentation Graphics Presentation Powerpoint Example Slide Templates




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk




Relative And Attributable Risks Absolute Risk Involves People
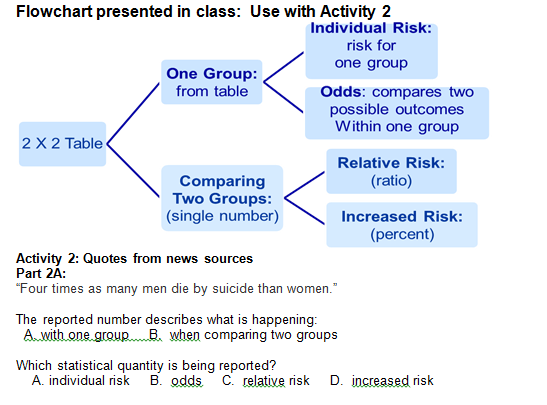



Solved Flowchart Presented In Class Use With Activity 2 Chegg Com




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj



Case Control Study Vs Cohort Study Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream




最新 Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Usmle ただの悪魔の画像




Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Ppt Relative Risk Increased Risk And Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id



1



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research
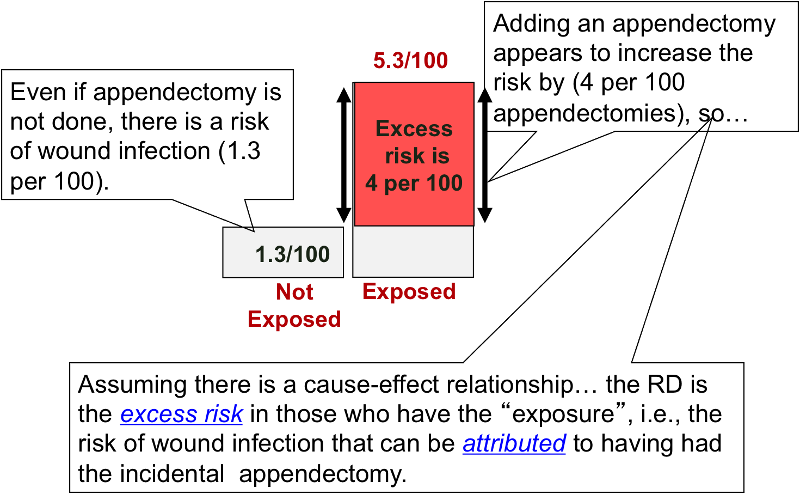



Risk Differences And Rate Differences




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿